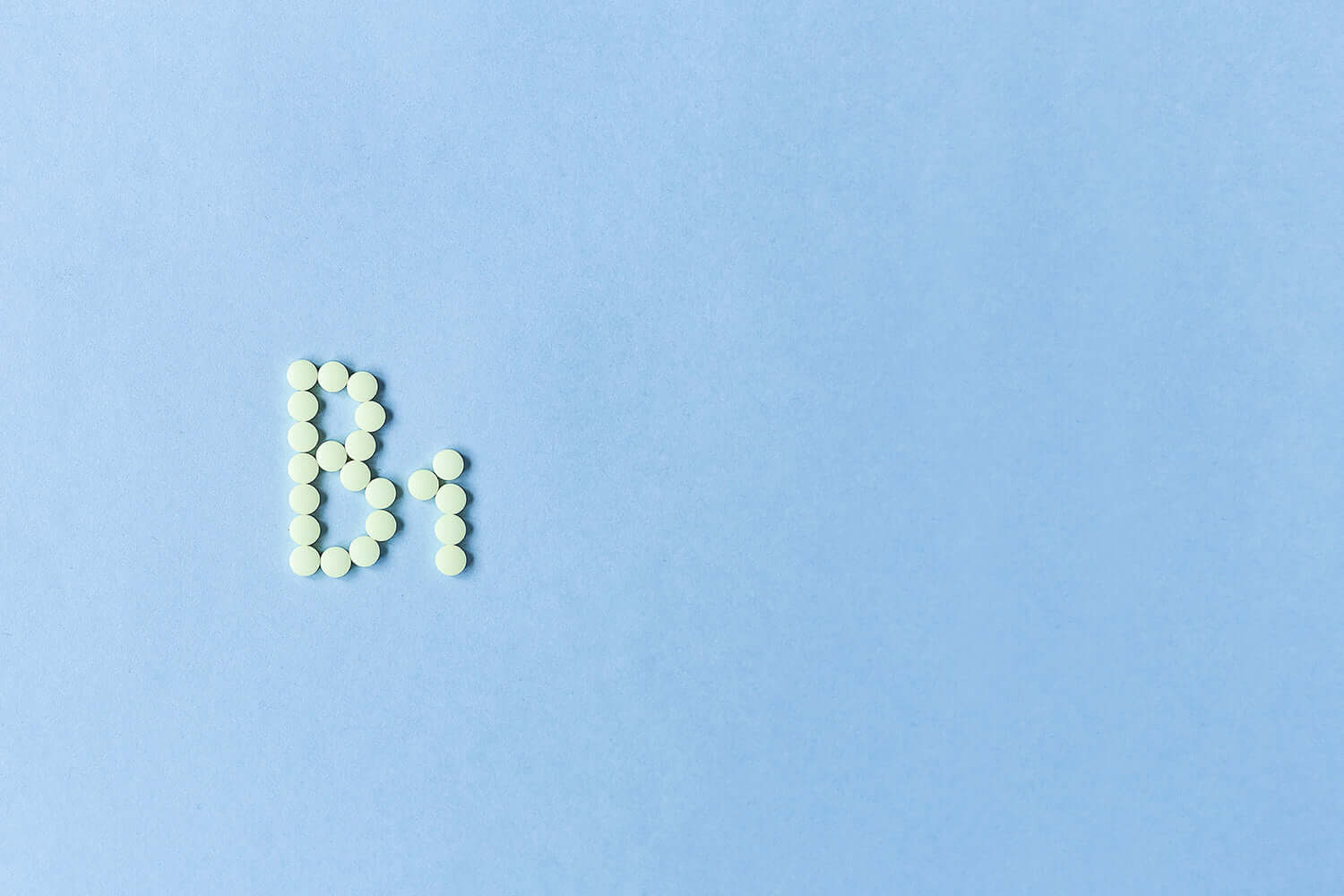
· By Jamal Ramsay
Essential Vitamins: B1 (Thiamin)
With all the vitamins that we need to get through our diets, it sometimes can be a bit confusing, and we may find ourselves asking "What is this vitamin good for again?" or "Did I get enough vitamin (insert vitamin here!) today?". Of course, having a varied diet is the BEST way to get enough of these essential vitamins (you could also try our range of shakes for a quick and easy solution), but the question still remains... What do all these vitamins do?
We're here to clear that all up for you. And we're going to dive head first into the Vitamin B complex. There are actually 12 vitamins in this complex, but we're going to start with numero uno, B1!
What is Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 which is also known as thiamin is part of a group of vitamins called water-soluble vitamins. These types of vitamins can’t be stored in our bodies, and if we have too much, our body cleverly gets rid of the extra amount when we urinate.
Why is Vitamin B1 Important?
So we know that it is, but why do we need it. Well it wouldn't be called an Essential Vitamin for nothing!! As one of Earth's natural energy boosters, Vitamin B1 has an important role in breaking down and releasing energy from food as well as keeping our nervous system and heart function healthy. Low levels of thiamin affect the cardiovascular, nervous, and immune system. There are many things that can lead to low B1 levels such as:
Poor Intake
- Diets primarily high in polished rice/processed grains
- Chronic alcoholism
- Parental nutritional without adequate thiamine supplementation
- Gastric bypass surgery
Poor Absorption
- Malnutrition
- Gastric bypass surgery
- Malabsorption syndrome
Increased Loss
- Diarrhoea
- Hyperemesis gravidarum
- Diuretic use
- Renal replacement therapy
Increased Thiamin Utilisation
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
- Hyperthyroidism
- Re-feeding syndrome
Diuretics can also lead to B1 deficiency.
What Foods Contain Vitamin B1?
Good sources of Vitamin B1 include:
- Peas
- Beans
- Wholegrain breads
- Some fortified breakfast cereals (always good to check the label!)
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Fruit (Nature's sweets!) such as bananas and oranges
- Meat such as pork or liver
What is quite important to note, this vitamin cannot be stored in the body, we need to include these foods in our diet every day, so be sure to eat plenty. This is where a way to fight low energy levels in females, such as our energy boosting vegan protein powder.
Remember... variety is the spice of life (in nutrition anyway ?)
SOURCES
At jrny, we are made up of a team of Sports Scientists and Registered Nutritionists. We want to make sure that we’re not just putting up the pseudo-science you’d see on other sites. If any of our staff put anything on our blog that relates to your health, you can bet that it is backed by evidence-based science! It always will be. That’s our commitment to you.

The information in this post was adapted from information provided by Registered Associate Nutritionist Sarah Tipping. Follow her @eatingwellwithsarah.
